The Future and Now of 3D Printed Food
3D printing isn’t just for plastic parts and prototypes. Almost anything can be 3D printed, including houses, human organs, and yes, even food. The technology for 3D printing food is just walking out of its infancy, with unlimited potential to change our world and improve our relationship with food in the future.
This article discusses the latest developments in 3D printed food, as well as what the future holds for this fascinating technology. Learn where you can eat professional 3D printed cuisine in restaurants, or how to start 3D printing your own food at home. It’s certainly not a cheap hobby, but 3D printed food is the ultimate nerdy luxury.
How does 3D Printing Food Work?
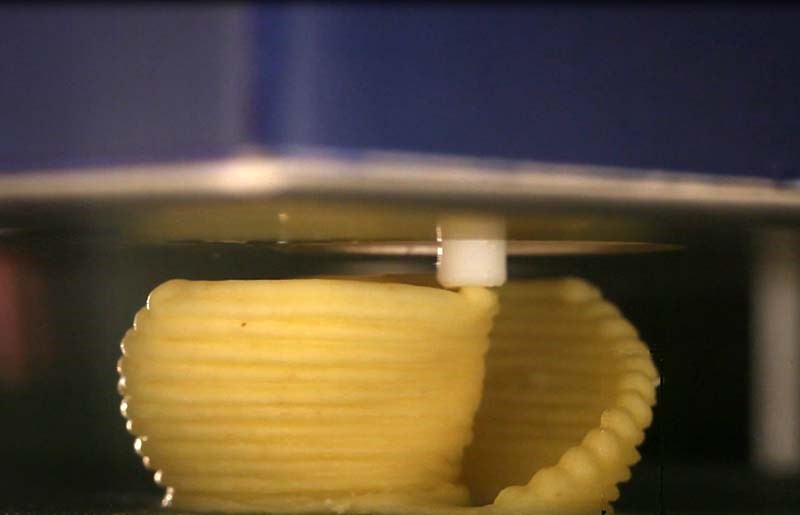
Like FDM (Fused Deposition Model) printers that use plastic filament, 3D food printers work by printing one layer at a time. Layers can be under 1mm small or much larger, depending on the application.
Instead of plastic, 3D printers made for food use different filaments. The Foodini, for example, uses fresh ingredients loaded into capsules. Chocolate printers obviously use melted chocolate, while confection printers use sugar. Dried, powered food may also be used, as may purees.
Basically, 3D printers use any soft material. Some foods, like chocolate, are ready to eat once they cool. Others, like 3D printed pizza, still require baking.
Is 3D Printed Food Safe?
3D printed food is just as safe as “real” food. So long as your ingredients are safe and your utensils are clean, then it’s safe to eat 3D printed food. Using old ingredients or a dirty 3D printer is still dangerous, just as it would be with traditional food prep.
3D Printed Food Today
Today, it’s possible to sit down at a fancy restaurant and eat an entire meal made from 3D printing. It’s also possible to print 3D meals at your home if you can stomach the price of a new printer.
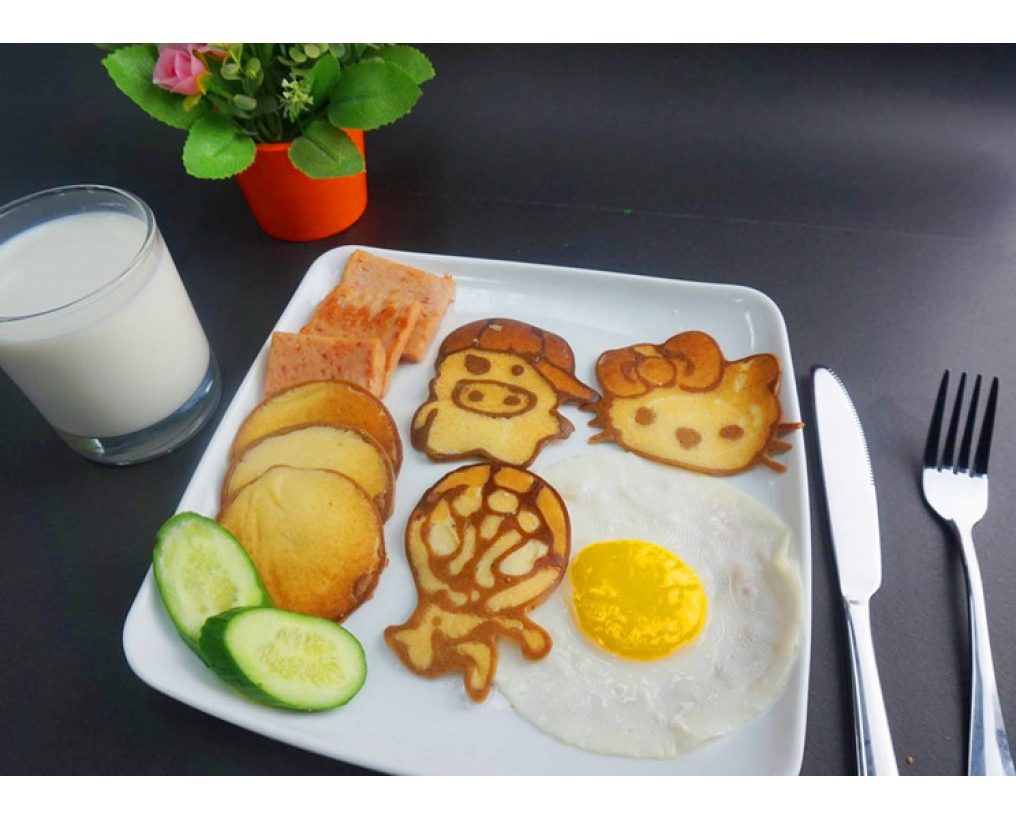
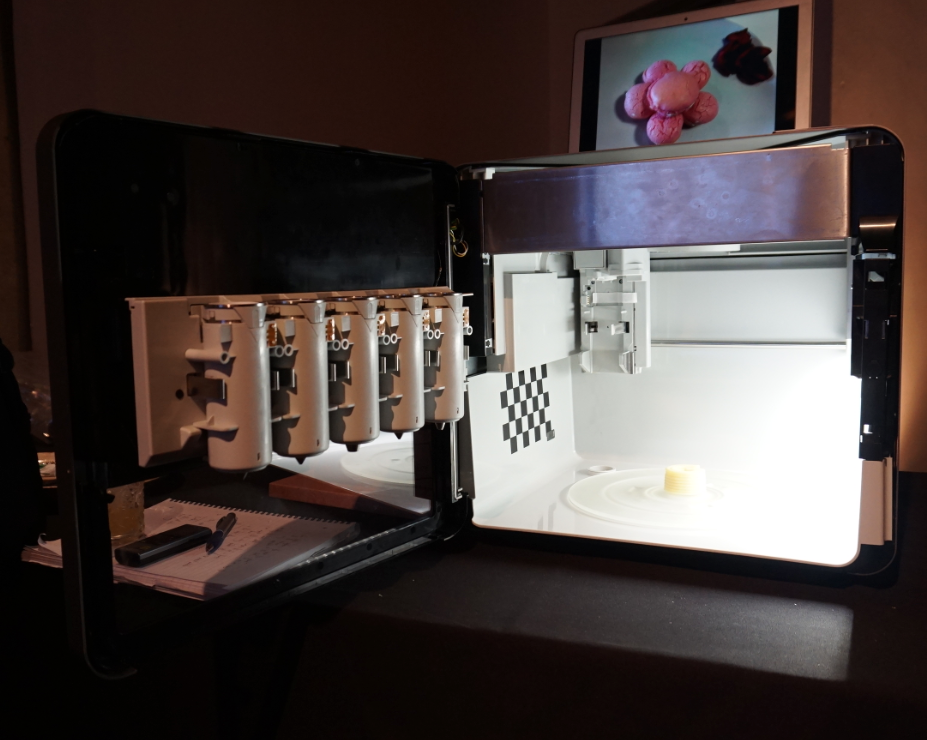
We already mentioned that the Foodini, made by Natural Machines, allows chefs to 3D print both sweet and savory dishes from fresh ingredients loaded directly into canisters. This machine makes pizza, burgers, noodles, candy, and much more.
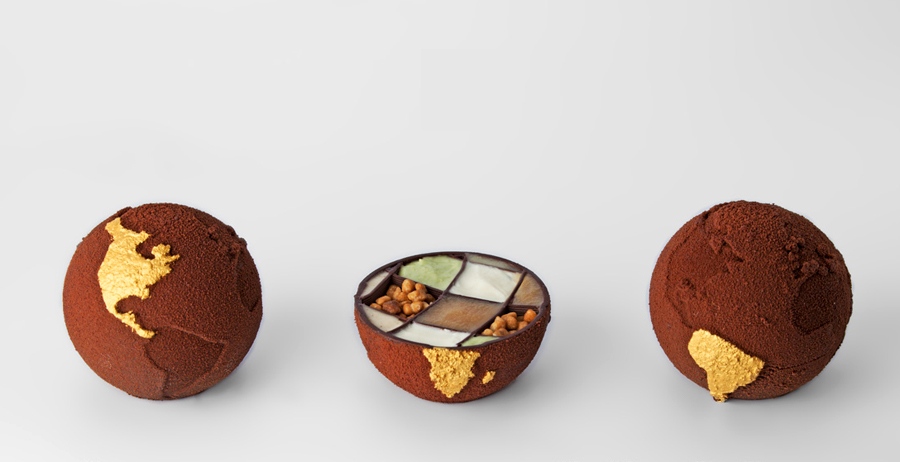
Until recently, desserts were the most common 3D printed foods. That’s because ingredients like sugar and chocolate are perfect for 3D printing. Both liquify at relatively low temperatures, and both solidify quickly at room temperature. 3D printing allows for incredibly precise results that would be impossible by hand or mold. Companies like 3D Systems and Choc Edge specialize in confection-based 3D printers.
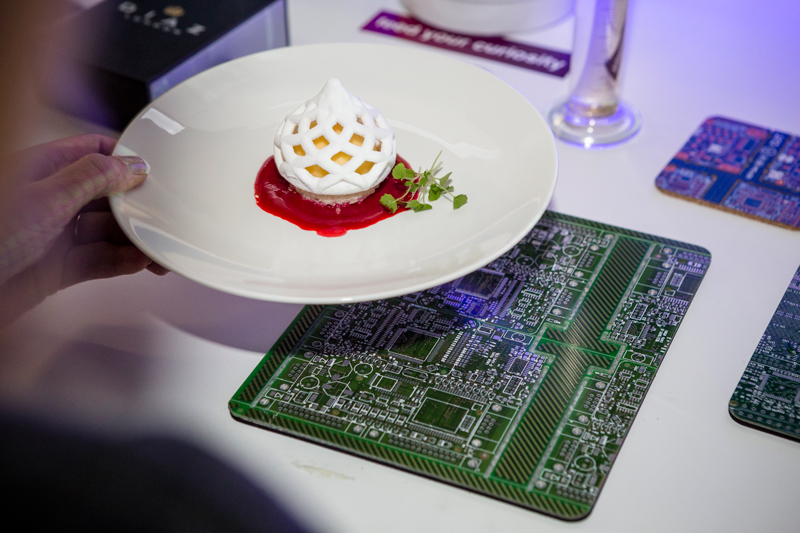
Unfortunately, there aren’t many restaurants using 3D printing yet, but a few pioneers do exist. Food Ink, for example, has locations in both London and Barcelona where the whole menu is 3D printed. Spain, and Barcelona in particular, is a hub for 3D printed cuisine and features several 3D eateries. At Miramar, one such restaurant in Spain, chefs use 3D printing to achieve intricate plating designs. Melisse in Santa Monica also offers 3D printed menu items.
3D Printed Food in the Future
At the moment, 3D printed meals are little more than a novelty. The machines are usually too expensive for home use, and the restaurants that serve 3D printed meals are equally as difficult to access for the average person. So what’s the point of 3D printed food if hardly anyone can afford it?
3D printed food has tremendous potential to make a positive impact on the environment and our health. To start, since 3D printed food is made to order in portion sizes we choose, printing our food stands to prevent a lot of waste.

Open Meals, creators of the FoodBase 3D food printer, want to make the process fun and easy for average consumers
Next, energy, time, and money will be saved if we begin shipping 3D food ingredients in dehydrated, power form. Imagine getting ingredient refills delivered to your house in light, compact powder. An “apple” would weigh grams instead of ounces.
In addition to reducing food waste and improving efficiency, 3D printed food has the potential to help people overcome medical conditions. One such condition is dysphagia, which makes it difficult to eat hard or crunchy foods. 3D printing has potential to create familiar-looking and -tasting food in a much softer form for these individuals.
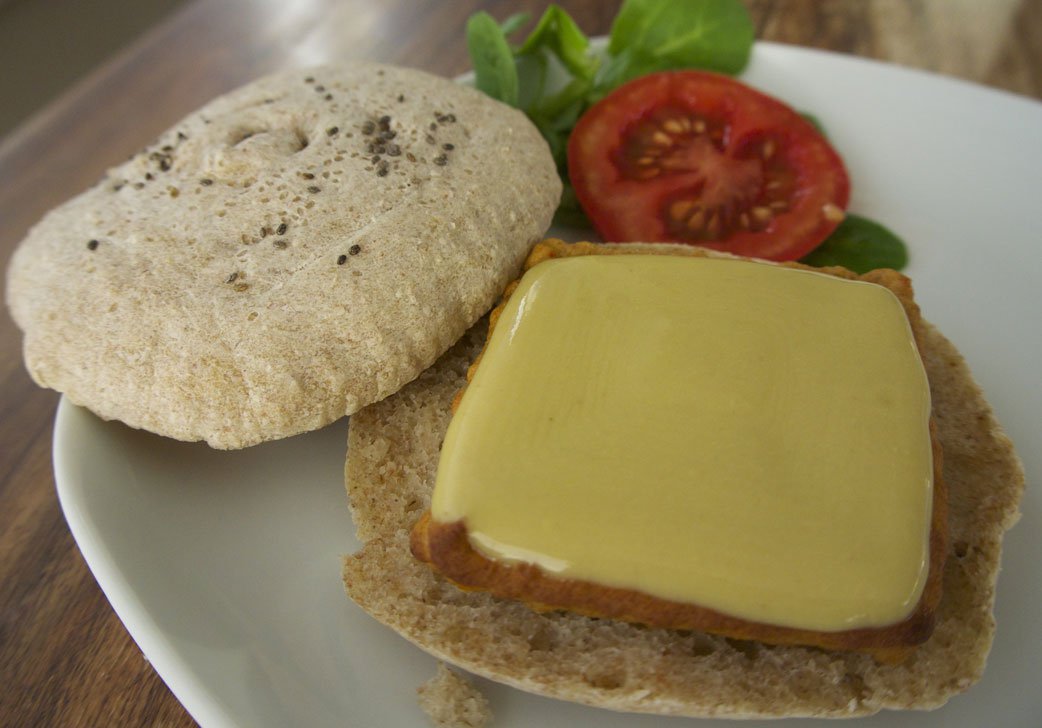

This chicken sandwich looks and tastes just like a traditional sandwich, but is much softer and easier to eat
The future of 3D printing also assumes that we will also be able to customize nutrient content for our meals. It will be almost impossible to become deficient in any key vitamin or nutrient when you have strict control over the nutrition of your food.
What to Expect
Today, 3D printed food is a luxury enjoyed by a lucky few. In the future, however, 3D food printers may be in every household, helping solve real-world problems like nutrient deficiency and food waste. Until then, we’ll keep you posted about the latest updates surrounding this exciting technology.